[sonaar_audioplayer albums=”243016, 243069, 243091, 243115, 243151, 243173, 243195, 243238, 243291″ progress_bar_style=”default” wave_bar_width=”1″ wave_bar_gap=”1″ player_layout=”skin_boxed_tracklist” show_track_market=”true”][/sonaar_audioplayer]
The UAE has been experiencing a sudden surge of 11.7% in malware detections since January 2024. The trend is more or less similar among most of the EMEA countries. They are facing increased malware and ransomware attacks. However, the conditions in MENA nations are worse than in EMEA countries. As per the report, Bahrain (63.2% malware detection) tops the list of MENA countries on the radar of threat actors. Egypt is not far behind and has managed to be in the second spot (42.6%)
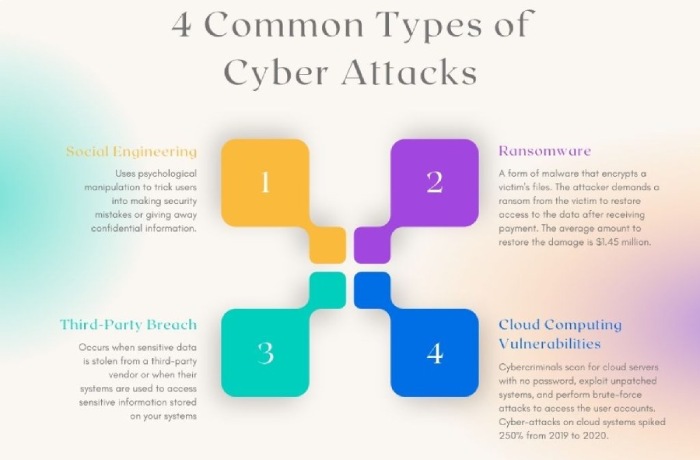
According to cybersecurity experts, the UAE is now a ‘prime target’ for ransomware attacks. Managed Service Providers, or MSPs, are more vulnerable to cyber threats like social engineering, supply chain attacks, and phishing.
Experts believe that an extra layer of protection is a must, given the current scenario, especially in the MSP infrastructure. For example, using advanced endpoint protection solutions, implementing all-encompassing security strategies, and organizing regular security awareness training can help prevent ransomware attacks to a great extent.
The current global scenario
Small and medium-sized businesses are prone to ransomware attacks, the most targeted industries being healthcare and government. As per the above report, in the first quarter of 2024, around 10 new ransomware groups were formed that claimed responsibility for about 84 global cyberattacks.
Out of these 10 ransomware attackers, 3 are the primary contributors (LockBit, Black Basta, and PLAY), and they alone led about 35% of the attacks. The most concerning part of the report is the 32% surge in ransomware detections from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024. Credential compromises, social engineering, phishing, and vulnerability exploits are some of the most common attack vectors that hamper and damage the cybersecurity defense mechanism of MSPs.
A holistic approach to secure data is a must at this moment.
The report also emphasizes the latest cyber threat trends and thereby mentions the inclusion of generative artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs). Threat actors now rely on AI to carry out social engineering and automation attacks on victims.
Some of the most common AI-backed cyberattacks include deepfake business email compromise, malicious emails, deepfake extortion, malware generation, and KYC bypass. Also, on a deeper level, there are two types of malware attacks. One, in which the malware is created using AI, and two, in which the malware functionality also includes AI.
The ongoing cyber trend in the Middle East
In the first six months of 2024, the UAE’s monthly percentage of malware detections varied between 0.8% and 1.9%. But if you look at high-risk nations like Germany, France, or the United Kingdom, the percentage is much higher (as much as 9%). This indicates a cyber threat landscape that is still not prominent and can be curbed easily if proper mitigation steps are taken.
The UAE has also experienced a sharp spike in the percentage of users with malware detections. In January 2024, the percentage was around 17.6%. Soon, in February, the percentage escalated to 18.8%. In March, the numbers were 29.1% and 29.3% in April and May. This sudden spike in malware detections indicates the requirement for a robust, all-encompassing security setup.
Seven Seas Technologies in the UAE has recently faced the brunt of ransomware attacks. This sensational incident has exposed the UAE’s vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Egypt and Bahrain are also showing alarming increases in malware detection rates.
If we take a look at the global trends, then Bahrain, South Korea, and Egypt are the worst hit when it comes to malware attacks in the first quarter of 2024. In Q1 2024, a staggering 28 million URLs had been blocked at the endpoint.
A whopping 27.6% of the received emails in the inbox were found to be spam, with about 1.5% containing malicious phishing links or malware. This highlights the need for phishing protection, as the issue is quite concerning—evident from the 1,048 ransomware cases reported in the first quarter of 2024, marking a 23% increase from Q1 2023.
If we take a look at the overall cyber threat landscape, then the number of phishing email attacks increased by a whopping 293% in the first half of 2024 in comparison to the first half of 2023. This number alone is a major red flag in the world of cybersecurity. Social engineering attempts have increased by 5% since the first half of 2023.
Also, the report suggests that there has been a 47% spike in email attacks against organizations. Generative AI like FraudGPT and WormGPT makes things convenient for threat actors. They leverage AI as it not only saves a great deal of time but also offers polished, error-free content that can be used for phishing and social engineering purposes.
It would be wrong if we focus entirely on the cons of artificial intelligence. Although AI has been a boon for threat actors, it can also be deployed to mitigate the impact of cyberattacks. In fact, when used correctly, artificial intelligence can be deployed and blended with cybersecurity mechanisms in order to intercept cyberattacks. AI has the capability to offer round-the-clock attack detection and expert guidance so that you can adopt relevant response actions and prevent any kind of cybercrime.
The need of the hour is to create a robust defense mechanism and stay updated about the latest cyber threats. Training on regular intervals backed by failproof cybersecurity setups further enhances the level of security and safeguards your sensitive data from threat actors.
The UAE has taken its wobbling cybersecurity landscape into cognizance and has come up with three new policies that emphasize data security, IoT security, cloud computing, and cybersecurity operations.
The announcement was made by the head of the UAE Cybersecurity Council- Mohammed Hamad Al-Kuwaiti. He said that the key idea behind this policy deployment is to introduce strict security protocols for data protection, curb cyberattack incidents, and lessen the impact of cyberattacks.