Water System Attacks: The New Strategy Leveraged By Threat Actors!
There has been a steep rise in the instances of cyberattacks on water systems. Different nations, such as the US, Norway, and Poland, are facing the brunt of the increased interest of cybercrooks in water systems or blue gold. Cybersecurity experts believe that nation-state threat actors are behind these attacks on crucial infrastructures such as water systems across countries. Apart from state-sponsored hackers, ransomware groups are also taking a keen interest in water utility sectors around the world.
In April, threat actors managed to tamper with the management of a Norwegian flood gate. They hacked the systems to open the floodgate forcefully and kept pouring out a massive 500 litres of water every second. This continued for the next four hours, leading to a severe water crisis.
Such attacks are becoming increasingly frequent, serving as a staggering reminder that water systems are severely vulnerable to threat attacks. Cybercrooks use these attacks to make the most out of the already existing geopolitical tensions around the world.
Head of counter-intelligence in Norway, as well as cybersecurity experts, believe that Russian threat actors are responsible for such attacks on water systems. They believe that the attacks are designed to create a sense of panic among the population of the targeted nations. This is a way to send a loud and clear message that the perpetrators are capable of causing severe destruction.
Something exactly similar has happened with Polish people as well. One of the largest Polish cities was recently under cyberattack. The hackers tried to disrupt the water supply of the entire city, thereby creating unrest and fear among the Polish people. But with proper systems in place, Poland managed to foil the threat attack.
Poland has been investing heavily in cybersecurity ($800 million). Their proactive measures and advanced preparations enable them to prevent 99% of the threat attacks. The Polish government, too, has blamed Russia-backed threat actors for this cyberattack.
Meanwhile, Russia has vehemently denied its involvement in these cyberattacks on crucial infrastructural setups.
The US, too, has been experiencing cyberattacks on water utility systems for the past 5 years. Industry reports, the Internet Criminal Complaint Center by the FBI, and government reports collectively suggest that both wastewater and water utility systems are being targeted repeatedly across the US. As per the reports of the Water Information Sharing and Analysis Center or ISAC, almost 19% of the water utilities in the US have been under cyberattacks within the first quarter of 2025.
Why are threat actors targeting global water utility systems?
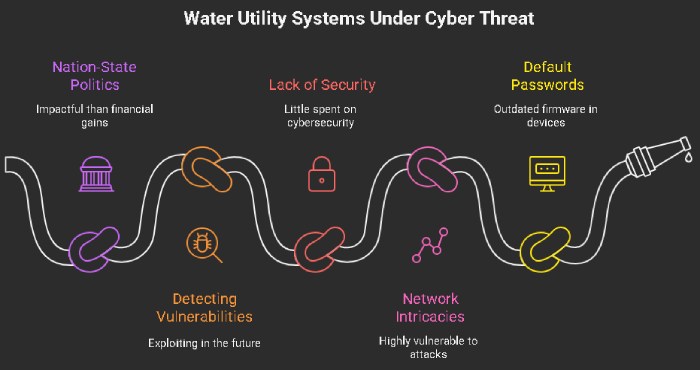
Since 2023-24, threat actors have been increasingly targeting critical infrastructures globally. But recently, water systems have been getting more attention from cybercrooks. This is so because attacks on water systems can impact the nation-state politics deeply, which matters way more than just some petty financial gains.
For example, a threat group with alleged connections with China attacked the water and power systems in Massachusetts and managed to go undetected in the systems for almost a year! Such attacks are aimed at detecting vulnerabilities across the infrastructural systems of a country and then exploiting the same in the future to design massive cyberattacks.
Another reason why cybercrooks target the water systems is the lack of a strong security system. Most of the time, these systems spend very little on cybersecurity mechanisms. Also, the intricacies across the networks make the water systems highly vulnerable to threat attacks. Besides, most of these devices use default passwords and use outdated firmware.
What next?
The sharp rise in cyberattacks on water systems highlights that safeguarding critical infrastructure is no longer optional. Governments, global security agencies, and utility providers must collaborate and rethink their cybersecurity strategies to strengthen digital defenses. Water utility providers, in particular, need to remain highly vigilant, as they are increasingly being targeted by cybercriminals. Strong measures such as advanced phishing protection and proactive monitoring are essential to minimize risks and ensure the security of these vital systems.
Water utility operators must prioritize cyber resilience at all costs. They must start by upgrading the outdated systems and should also enforce stronger authentication practices to prevent any major cyber disruption in the future.
Cybersecurity agencies, governments, and water utility providers must collaborate to combat the cybercrooks who operate across borders. To foil their malicious attempts, these agencies should invest their time, money, and energy in proactive monitoring, real-time reporting, and cross-border intelligence sharing.
Governments must recognize the importance of investing heavily in developing robust cybersecurity mechanisms. They must allocate substantial budgets to safeguard their water infrastructure.
Public awareness and voluntary cybersecurity assistance can also play a key role in securing crucial infrastructures such as water, power, and other critical services. Nations must treat water infrastructure vulnerability as a public safety issue. Only then can they make adequate preparations both technically and socially to thwart such threat attempts.