Spear Phishing is a type of phishing attack which generally targets “Whales” or “high-level organizational actors” such as C-suite executives (e.g., CEO, CFO, CIO, etc.) or upper management to steal financial and sensitive or confidential information from unsuspecting top-level management. Spear phishing data breaches account for more than half of the phishing scams worldwide, which occur every year. Verizon reports elucidate that a high proportion of these data breaches begin with a directed phishing campaign targeted against an enterprise. Although corporations deploy sophisticated phishing prevention software to safeguard their data, they remain vulnerable because of human error, which allows adversaries to bypass such security measures, including anti-phishing solutions.
Even today, most security professionals blame human failure as the main weak link in organizational security. “Human” here refers to users of technology with the exception of adversaries. Although major enterprises invest a considerable amount of capital on cybersecurity measures, news headlines regularly report new spear-phishing scams. There is no doubt that ignorance of employees and executives is a significant reason such attacks are successful.
Such a situation is dangerous and untenable in this digital age, where cyber espionage is a matter of ‘when’ rather than that of ‘if.’ We can understand the severity of the situation from the fact that scammers create approximately 1.5 million new phishing sites every day. Knowing about the circumstances of the case can help organizations prepare themselves and face such threats successfully.
Spear Phishing Statistics: An Unwelcome Trend
Statistics and data reports are one of the best ways of learning about the harsh reality of cyber warfare. The Russian interfering in the 2016 US Presidential election is famous, and it is also an example of how a state-sponsored social media campaign can aggravate social and political disruptions in another country
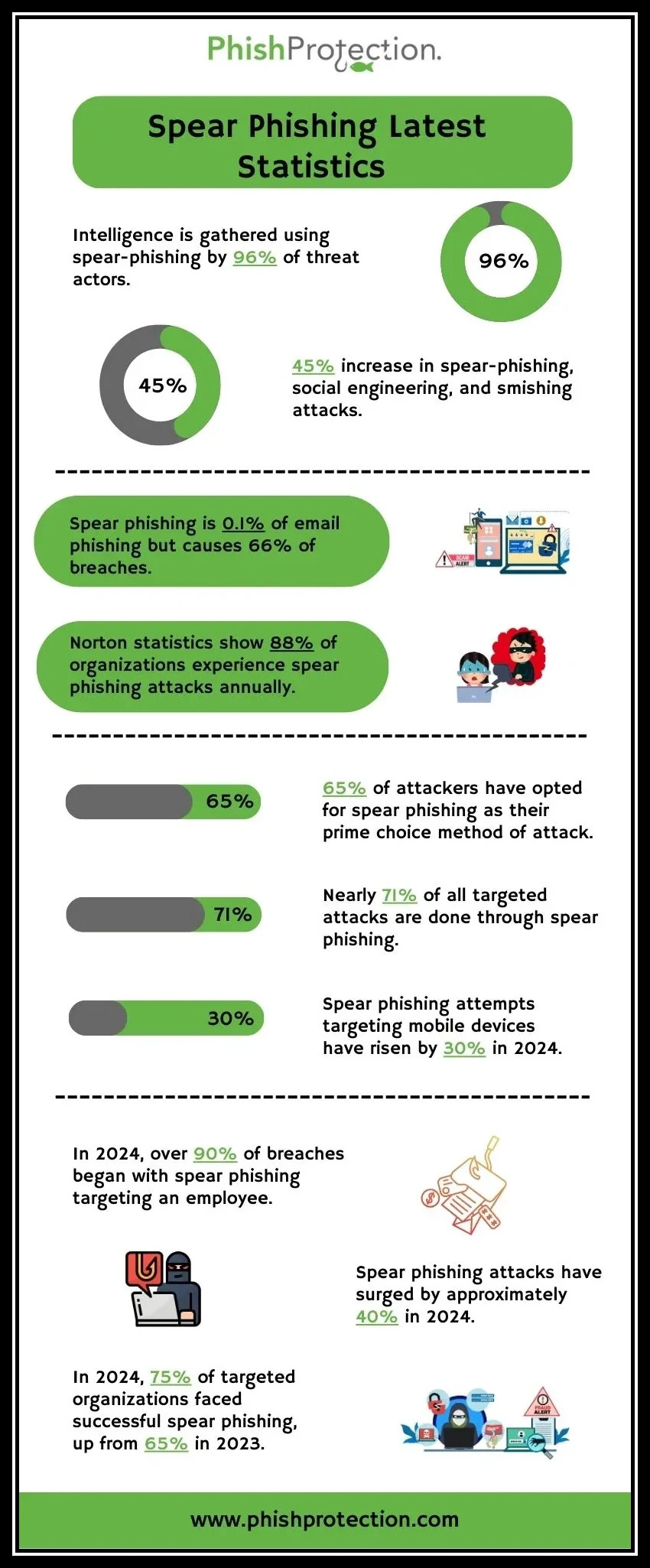
Given below are 13 spear-phishing statistics to make your case for email fraud protection:
- According to a report by Cofense, formerly known as PhishMe, around 91 percent of all cyberattacks begin with a spear-phishing email. Phishing has continued to be the most common form of attacks against businesses around the globe.
- According to the “State of the Phish Report, 2019”, which Proofpoint compiled from detailed phishing statistics based on multiple sources, including about 15,000 responses to the quarterly surveys on infosec professionals around the globe, 83 percent of the global infosec respondents experienced phishing attacks in 2018. The numbers showed an increase of seven percent from that in 2017. Reports of credential compromise due to these attacks also rose by 70 percent from 2017.
- It seems that hackers are taking active measures to thwart our attempts at countering their attacks with spear phishing prevention softwares. As per the latest “Phishing Activity Trends Report” released on January 2019, nearly half of all phishing websites are now being created using HTTPS encryption. This number is about a 900 percent increase since the end of 2016 and increases threat levels significantly. The report also says that phishing sites have taken to using more web page redirects to evade detection attempts.
- According to Norton Security, the USA experiences the highest volume of cybersecurity attacks in the world. Nearly 60 percent of American families have witnessed exposure to cyber fraud schemes according to research done by The Harris Poll and the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA). Wombat Security’s State of the Phish 2018 also reported that 76 percent of organizations and businesses were targets of phishing attacks.
- The number of brands targeted is also on the rise, with the figure for September 2018 at 286, the highest in a month since November 2017. The Online Payments Sector was targeted the most by phishing attacks in Q3 2018, followed by SAAS/ webmail and financial institutions. The latest Phishing Activity Trends Report revealed this finding.
- As per Phish Labs’s 2018 “Phishing Trends and Intelligence Report,” phishing attacks by hackers mimicking SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) platforms increased by a whopping 237 percent in 2017.
- Verizon said that phishing and pretexting accounts for a high number of social incidents and breaches. Verizon’s 2018 Data Breach Incident Report puts the numbers at 98 percent of social incidents and 93 percent of breaches as being represented by phishing and pretexting.
- The Microsoft Security Team released a report, after extensive scanning of over 470 billion business email messages that have been received by the customers of its Office 365 platform, which states that malicious phishing attacks have increased by over an alarming 250 percent. The report also uncovered more bad news; it says that hackers are growing in proficiency, which makes their attacks harder to detect and counteract.
- Thirty-four percent of all cyber-attacks on organizations involved insiders, according to Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report 2019. The report, which is compiled from a comprehensive summary of statements by public and private entities around the globe of data breaches, also states that 43 percent of these cyber-attacks target SMBs. This high number of attacks on small businesses proves the fact that anyone can be a target no matter what their size is.
- The Verizon report also uncovers that C-Level executives in an organization are targeted 12 times more by social engineering attacks than other employees. This particular report confirms that attackers are doing their surveillance and profiling with high proficiency.
- The astronomical amount of money lost to cybercriminals is going to increase. According to Juniper Research 2016, the cost of cybercrime and data breaches will rise to $2.1 trillion by 2019.
- IBM estimates that a data breach by hackers has an average financial cost of $3.86 million. Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams account for over $12 million in losses, according to a survey conducted by the FBI.
- Last year’s report from Lookout states that about 56% of mobile device users have received and clicked on a phishing URL.
Conclusion
It might seem obvious, but these reports show that there is a significant knowledge deficiency with regards to awareness and proper education of employees and executive users when it comes to phishing.
Phishing attacks – primarily targeted phishing attacks like whaling and spear phishing – continue to be successful because they are very effective. They also remain lucrative at the same time as a successful spear-phishing attack could net the attacker up to $1.6 million (Keepnet Study 2017). What’s more, it is not just individuals but even government-funded hackers who are directly or indirectly involved in spear-phishing attacks such as the hacking of Ukraine’s power grid.