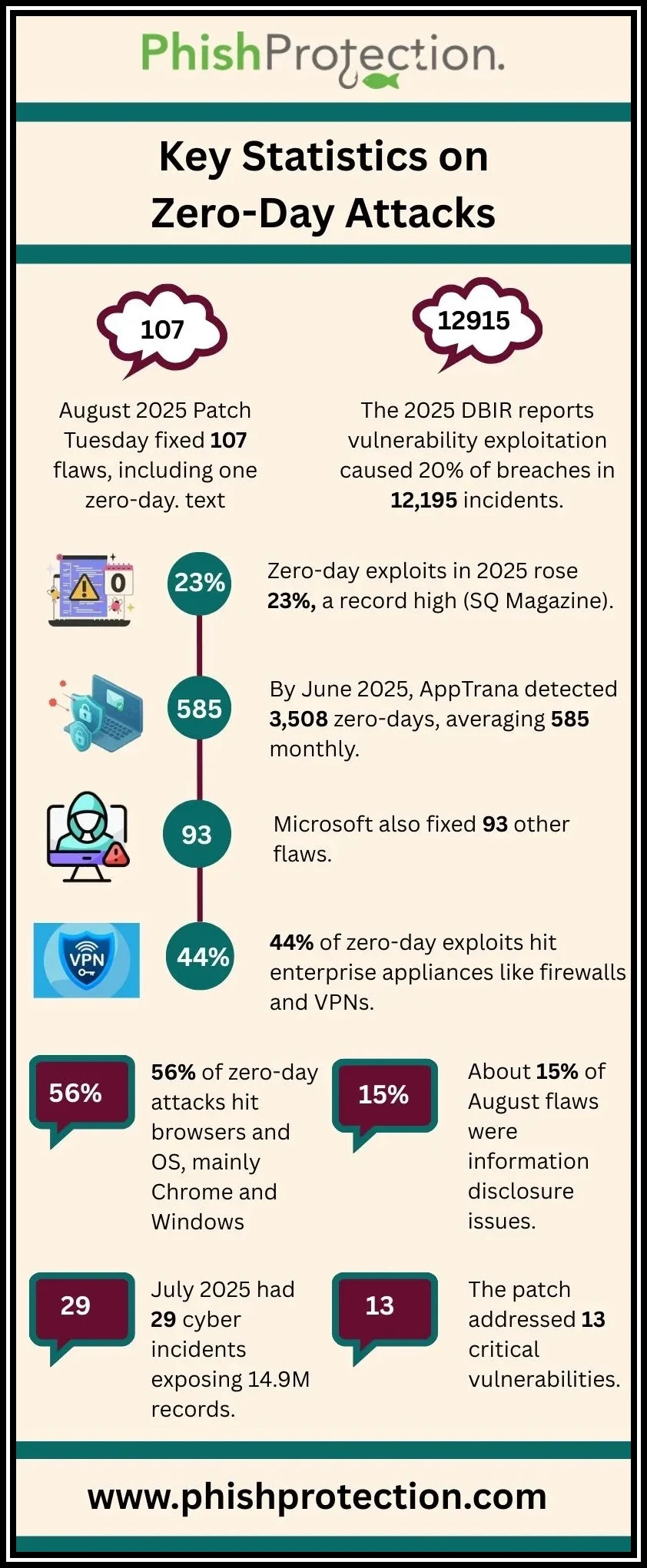
In the ever-evolving domain of cybersecurity, zero-day threats represent some of the most sophisticated and dangerous challenges facing organizations worldwide. A zero-day vulnerability is a previously unknown software vulnerability that has not yet been patched or disclosed publicly. Cybercriminals exploit these zero-day vulnerabilities through a zero-day exploit, often before software vendors can issue security patches or mitigation measures. These exploits can trigger severe consequences, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and infiltration by advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Characteristically, zero-day threats leverage the fact that no defense mechanism is prepared to detect or block an exploit as it strikes for the first time. Unlike known threats mitigated by signature-based detection, zero-day attacks require more dynamic and adaptive methods such as behavior-based detection, machine learning security, and advanced heuristic analysis. Moreover, some exploits are fileless malware that reside in memory, evading traditional malware detection tools. This invisibility makes them highly perilous, necessitating a multi-layered approach to threat prevention.
Common Attack Vectors and Exploitation Methods
Zero-day exploits infiltrate networks and devices through various attack vectors, often integrating with exploit kits and other toolsets that automate vulnerability discovery and exploitation. The most common vectors include:
- Application security flaws: Attackers exploit software vulnerabilities in widely used applications or operating systems.
- Network security gaps: Unsecured or insufficiently monitored network traffic can be a conduit for zero-day payload delivery. Tools like network traffic analysis and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) from vendors such as Palo Alto Networks and Cisco are crucial in identifying suspicious patterns indicative of a zero-day attack.
- Email and web-based attacks: Targeted phishing or drive-by downloads deliver malicious payloads that exploit zero-day vulnerabilities. Implementing sophisticated phishing protection systems is essential for reducing threats posed by harmful emails and misleading links.
- Exploit kits: These are automated frameworks that scan for vulnerabilities and deploy zero-day exploits accordingly.
Once inside, attackers may use fileless attack techniques to avoid detection by traditional endpoint antivirus solutions. Attackers can then establish persistence, launch data exfiltration, or escalate privileges as part of an advanced persistent threat campaign, complicating incident response efforts.
The Importance of Threat Intelligence in Zero-Day Prevention
Threat intelligence plays a fundamental role in mitigating zero-day threats by offering actionable data about emerging vulnerabilities, exploit trends, and attacker tactics. Robust threat intelligence solutions aggregate information from global sensors, honeypots, and security analytics platforms, translating raw data into meaningful insights. Leaders in this field, such as FireEye, Mandiant, and RSA Security, provide comprehensive threat feeds that inform security teams about zero-day exploits and evolving cyberattack methodologies.
Incorporating real-time threat intelligence into security infrastructure supports:
- Enhanced vulnerability assessment to prioritize patch management and exploit mitigation before attackers can weaponize software flaws.
- Informed risk management decisions by mapping zero-day threat landscape changes to organizational assets.
- Strengthening cyber defense postures via integration with security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms from vendors such as Splunk or Palo Alto Networks Cortex.
This intelligence-driven approach helps close the window of exposure and supports proactive defense strategies critical for effective zero-day threat prevention.
Implementing Advanced Endpoint Protection Solutions
Given that endpoints often serve as main entry points for zero-day exploits, advanced endpoint protection strategies are indispensable. Endpoint security platforms from cybersecurity leaders like CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, VMware Carbon Black, and Symantec offer a blend of technologies, including endpoint detection and response (EDR), real-time monitoring, and exploit mitigation capabilities.
Key features of advanced endpoint solutions include:
- Behavioral analytics: Detects anomalies in endpoint behavior suggestive of zero-day exploit activity.
- Sandboxing: Isolates suspicious files in a controlled environment to observe unknown behavior safely, enabling detection of fileless malware or novel ransomware strains.
- Heuristic analysis and machine learning security: Utilize AI to discern patterns and predict zero-day exploit attempts without reliance on signatures.
- Integrated ransomware protection: Anti-exploit measures that prevent vulnerability exploitation at the point of attack.
Incorporating robust endpoint protection, as offered by McAfee, Trend Micro, and Kaspersky Lab, with network security solutions enhances an organization’s overall cyber defense architecture, enabling swift incident mitigation and reducing dwell time for zero-day intrusions.
Role of Behavioral Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Traditional cybersecurity methods often falter against dynamic zero-day threats that lack known signatures or recognizable artifacts. Hence, behavior-based detection and sophisticated behavioral analytics become pillars in zero-day threat prevention. By establishing baselines of normal user and system activities, security solutions can flag deviations indicative of stealthy attacks.
Advanced artificial intelligence cybersecurity models analyze real-time behavioral data across endpoints and networks, facilitating early threat detection. For instance, Darktrace and Cybereason harness AI-driven cyber threat hunting capabilities to continuously scan for subtle signs of compromise, such as unusual process executions or network connections.
Integrating behavioral analytics with SIEM platforms enhances contextual understanding of alerts, enabling faster, more accurate incident response. Additionally, combining this approach with penetration testing and continuous vulnerability assessment ensures that organizational security evolves dynamically with the shifting threat landscape.
In summary, behavioral analysis coupled with anomaly detection offers a robust complement to traditional cybersecurity tactics, targeting the elusive characteristics of zero-day exploits and supporting comprehensive cyberattack prevention frameworks.
Statistical Data: Zero-Day Exploit Impact and Mitigation Trends
- Average zero-day exploit lifespan before detection: 7 days
- Percentage of zero-day attacks leveraging fileless malware: 35%
- Effectiveness increase of endpoint protection with AI-enhanced detection: 45%
- Reduction in incident response time using integrated threat intelligence and SOAR: 60%
- Organizations adopting zero-trust security frameworks incorporating zero-day prevention: 70%
Source: FireEye M-Trends Report 2023, CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2024
Effective Patch Management and Vulnerability Assessment
In the dynamic threat landscape, managing zero-day vulnerabilities effectively requires a robust patch management strategy combined with continuous vulnerability assessment. Patch management serves as a fundamental aspect of exploit mitigation by ensuring that software vulnerabilities discovered, whether known or suspected, are promptly addressed through security patching. Organizations leveraging cybersecurity frameworks such as those recommended by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) integrate comprehensive patch management processes with vulnerability assessment tools to identify zero-day exploits before they are exploited in cyberattacks.
Leading cybersecurity companies like Microsoft Defender, Symantec, and Trend Micro provide automated patch management solutions that integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for real-time monitoring and response. These solutions enable organizations to reduce the attack surface by identifying critical software vulnerabilities and deploying patches swiftly, thereby enhancing data breach prevention capabilities.
Vulnerability assessments, performed through penetration testing and network traffic analysis, help detect weaknesses, including those that could be exploited by exploit kits or advanced persistent threats (APTs). Tools from CrowdStrike and FireEye combine cyber threat hunting and behavioral analytics to identify potential zero-day vulnerabilities hidden in complex systems. The integration of machine learning security models with heuristic analysis further improves the detection of subtle exploit attempts, including fileless malware, which can circumvent traditional signature-based detection methods.
Network Security Strategies to Detect and Mitigate Zero-Day Attacks
Network security remains paramount in detecting and mitigating zero-day attacks through a multi-layered defense approach. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), advanced firewall solutions from Palo Alto Networks and Fortinet, and real-time network traffic analysis are essential components for thwarting zero-day exploits at the perimeter and within internal segments.
Deployment of sandboxing environments, as seen in solutions by McAfee and Kaspersky Lab, enables suspicious files or behaviors to be analyzed safely, providing malware detection and ransomware protection without risking live systems. Alongside, behavioral analytics and machine learning-powered threat detection facilitate the identification of novel attack patterns that diverge from typical network behavior, essential for detecting stealthy fileless malware attacks or exploit kit activity.
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms offered by RSA Security and Cybereason automate incident mitigation processes by correlating alerts from diverse threat feeds, enabling rapid detection and containment of zero-day vulnerabilities before they escalate into breaches. Additionally, adopting zero-trust security architectures limits lateral movement of attackers by enforcing strict access controls, reducing exposure even if initial intrusion occurs via unknown or unpatched software vulnerabilities.
Incident Response Planning and Zero-Day Threat Recovery
Incident response planning specific to zero-day threats focuses on preparation and rapid action following the identification of exploits unknown prior. Cyber defense teams, utilizing endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools from companies such as SentinelOne, Carbon Black, and Sophos, maintain visibility of endpoint protection status and suspicious activity.
Organizations invest heavily in incident response workflows that leverage cybersecurity frameworks and threat intelligence sharing from Mandiant and Check Point Software Technologies. These workflows emphasize real-time monitoring, accurate threat detection through signature-based and behavior-based detection, and the incorporation of advanced forensic analysis for incident mitigation.
Effective recovery from zero-day incidents involves coordinated efforts across IT, security, and risk management teams to apply security patching, reset compromised credentials, and reinforce application security measures. Regular cyber threat hunting enhances organizational preparedness by proactively searching for indicators of compromise related to zero-day vulnerabilities. The continuous refinement of incident response plans helps minimize damage from exploits, reducing downtime and preventing large-scale data breaches.
Leveraging Machine Learning and AI in Zero-Day Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence cybersecurity solutions have revolutionized zero-day exploit detection by introducing capabilities that surpass traditional methods. Machine learning security models excel at identifying anomalies in network traffic, endpoint behavior, and application usage—crucial for discovering zero-day vulnerabilities and preventing advanced persistent threats.
Darktrace and Bitdefender utilize proprietary AI-driven behavioral analytics combined with heuristic analysis to detect previously unseen malware variants and fileless malware attacks. By continuously learning from threat feeds and cybersecurity telemetry, these systems adapt to emerging tactics used by cybercriminals in exploit kits and ransomware campaigns.
Incorporating machine learning with endpoint protection and network security systems enhances malware detection and threat prevention, supporting automated incident response. Security platforms that provide integrated Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) capabilities enable organizations to gain contextual insights and accelerate remediation efforts, decreasing dwell time of zero-day exploits.
Best Practices for Employee Training and Security Awareness
Technological solutions alone cannot eradicate zero-day vulnerabilities; human factors play a pivotal role in cybersecurity. Comprehensive employee training programs that focus on security awareness mitigate social engineering risks, which often precede the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities.
Organizations should implement continuous education on identifying phishing emails, suspicious network behavior, and compliance with zero-trust security models. Companies like Cisco and Check Point Software Technologies offer specialized training modules that incorporate simulations to reinforce practical understanding. Embedding threat intelligence into training ensures that employees remain informed about the evolving threat landscape.
Furthermore, encouraging a security-first culture improves incident reporting responsiveness and adherence to cybersecurity policies. Regular penetration testing exercises, combined with security awareness training, enable organizations to identify and address weaknesses proactively, thereby closing gaps that could be exploited by zero-day vulnerabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Effective patch management combined with continuous vulnerability assessment is essential for reducing exposure to zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Network security strategies, including intrusion prevention systems, sandboxing, and behavioral analytics, are critical for detecting and mitigating zero-day exploits.
- Incident response planning that incorporates real-time monitoring, threat intelligence, and endpoint detection and response accelerates recovery from zero-day threats.
- Machine learning and AI enhance zero-day threat detection by identifying anomalous behavior and adapting to emerging cyber threats.
Ongoing employee training and security awareness are vital components of holistic cyberattack prevention and risk management strategies.